As an Amazon Associate KitchenwareSets.com earns from qualifying purchases.
How Induction Cooktops Work: Electromagnetic Heating, Efficiency, and Benefits
Induction cooktops represent a cutting-edge approach to modern cooking, but how exactly do they work? If you’re intrigued by the technology behind these sleek appliances or confused about their benefits and compatibility, you’re not alone. Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields heat pots and pans, offering rapid and efficient cooking.
Ever wondered why these cooktops are becoming so popular in kitchens around the world? Dive into our comprehensive guide to uncover the science behind induction cooking, explore its advantages over traditional methods, and find out how to choose the right cookware for your induction stove. From the basics of electromagnetic induction to practical tips for maximizing efficiency and safety, this article will answer all your pressing questions and more. Keep reading to master the art of induction cooking your culinary experience!
Key Facts:
1. Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly.
2. Only ferromagnetic cookware is compatible with induction cooking.
3. Induction cooking is up to 84% energy efficient compared to 74% for gas or electric stoves.
4. The cooktops surface remains cool to the touch enhancing safety.
5. Induction cooking offers precise temperature control and rapid heating.
The Science Behind Induction Cooking

Induction Cooktops Technology Diagram – source
The science behind induction cooking is fascinating and revolutionary. At its core, induction cooking harnesses the power of electromagnetic energy to heat your food quickly and efficiently. Unlike traditional cooking methods that rely on thermal conduction or radiation, induction cooking creates heat directly within the cookware itself.
What is Electromagnetic Induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which an electric current is produced in a conductor when exposed to a changing magnetic field. In the context of cooking, this principle is applied to generate heat in your pots and pans.
Here’s how it works:
- Copper Coil: Beneath the glass-ceramic surface of an induction cooktop lies a copper coil.
- Alternating Current: When you turn on the cooktops, an alternating electric current flows through this coil.
- Magnetic Field: This current creates an oscillating magnetic field above the cooktop surface.
- Eddy Currents: When you pot or pan on the cooktop, the magnetic field induces electrical (eddy) currents in the base of the cookware.
- Resistance Heating: These eddy currents encounter resistance in the metal, which generates heat.
This process happens instantaneously, allowing for rapid heating and precise temperature control.
How Do Induction Cooktops Generate Heat?
Induction cooktops generate heat through a process called resistive heating. When the e through the metal base of your cookware, they encounter resistance. This resistance causes the metal to heat up rapidly, which in turn heats the contents of your pot or pan.
It’s important to note that the cooktop itself doesn’t get hot. The heat is generated directly in the cookware, making induction cooking not only efficient but also safer than traditional methods.
The Role of Copper Coils in Induction Cooking
The copper coils play a crucial role in the induction cooking process. These coils are typically arranged in a circular pattern beneath the cooking surface. When an electric current passes through these coils, it creates a magnetic field.
The strength and size of this magnetic field can be controlled by adjusting the amount of current flowing through the coils. This allows for precise control over the cooking temperature, a significant advantage of induction cooking.
How E Heat the Cookware
Eddy currents are circular electric currents induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field. In induction cooking, these currents are induced in the base of your cookware.
The process works as follows:
- The changing magnetic field from the cooktop induces eddy currents in the cookware.
- These currents flow in circular paths within the metal.
- As the currents flow, they encounter resistance in the metal.
- This resistance causes the metal to heat up due to the Joule heating effect.
The heat generated by these eddy currents is then transferred to the food in the cookware through conduction.
How Induction Cooktops Remain During Cooking
One of the most remarkable features of induction cooking is that the cooktop surface remains relatively cool to the touch, during cooking. This is possible because the heat is generated directly in the cookware, not in the cooktop itself.
The glass-ceramic surface of an induction cooktop is not ferromagnetic, so it doesn’t interact with the magnetic field produced by the copper coils. As a result, it doesn’t heat up directly. Any warmth you might feel on the surface is residual heat transferred from the hot cookware.
This feature not only makes induction cooking safer but also easier to clean, as food spills are less likely to burn onto the surface.
Direct vs Heating in Traditional Cooktops
To truly appreciate the efficiency of induction cooking, it’s helpful to compare it with traditional cooking methods:
- Gas Cooktops: Gas stoves produce a flame that heats the bottom of the cookware. Much of the heat is lost to the surrounding air, making them less efficient.
- Electric Cooktops: These use a heating element that gets hot and transfers heat to the cookware through conduction. There’s a delay in heating and cooling, and energy is lost in the process of heating the element.
- Induction Cooktops: Heat is generated directly in the cookware, resulting in faster heating times and less energy waste.
This direct heating method is what makes induction cooking up to 84% energy efficient, compared to about 74% for traditional electric or gas stoves.
The Technology Behind Induction Cooktops
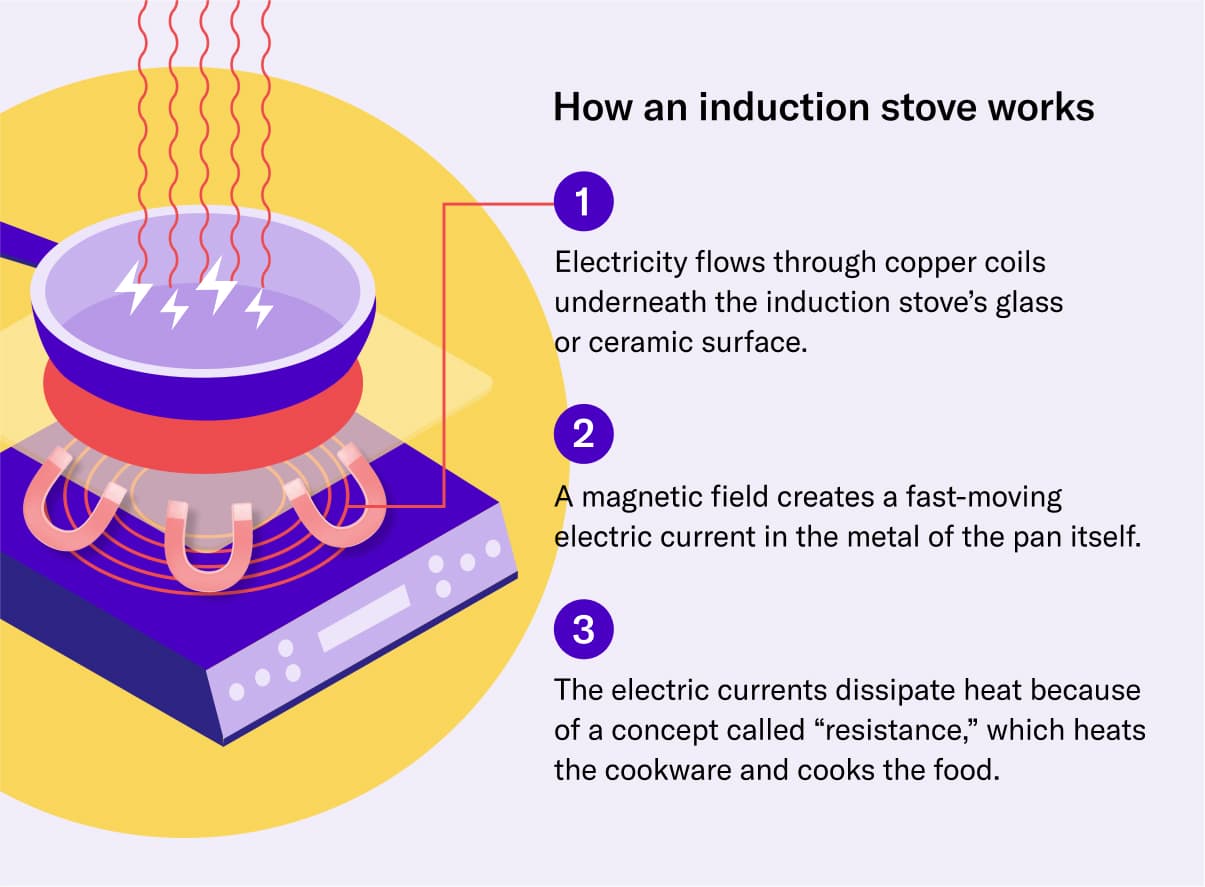
How an Induction Stove Works – source
The technology behind induction cooktops is a marvel of modern engineering, combining principles of electromagnetism with advanced electronic controls. Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of induction cooking technology.
The of Oscillating Magnetic Fields
At the heart of induction cooking technology lies the principle of oscillating magnetic fields. These fields are created by passing an alternating current through a copper coil beneath the cooktop surface.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Alternating Current: The cooktop is powered by an alternating current (AC) from your home’s electrical supply.
- Frequency Conversion: This current is typically converted to a higher frequency (usually between 20-100 kHz) by the cooktop’s electronics.
- Magnetic Field Generation: The high-frequency current flowing through the copper coil creates an oscillating magnetic field.
- Field Interaction: This field interacts with the ferromagnetic material in your cookware, inducing eddy currents.
The oscillation of the magnetic field is key to the efficiency of induction cooking. It allows for rapid changes in cooking temperature and precise control over the heating process.
Induction Heating Efficiency Compared to Other Methods
Induction cooking stands out for its remarkable efficiency compared to traditional cooking methods. Here’s tipss up:
| Cooking Method | Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Induction | 84% |
| Electric | 74% |
| Gas | 40% |
How Electromagnetic Fields Cookware
One of the most intriguing aspects of induction technology is how it specifically targets the cookware while leaving the surrounding area cool. This achieved through the careful design of the electromagnetic field.
- Field Concentration: The magnetic field is concentrated just above the cooktop surface.
- Cookware Detection: Many induction cooktops have sensors that detect when compatible cookware is placed on the surface.
- Field Activation: The field is only activated when it detects the presence of ferromagnetic material.
- Targeted Heating: The field interacts specifically with the cookware, inducing currents only in the pot or pan.
This targeted heating is what allows induction cooktops to be so efficient and safe. It’s why you can often place your hand on an active induction cooktop without getting burned (though we don’t recommend trying this!).
Understanding Resistance Heating in Ferromagnetic Cookware
Resistance heating is the final step in the induction cooking process. It occurs within the ferromagnetic material of your cookware.
Here’s how it works:
- Eddy Current Induction: The oscillating magnetic field induces eddy currents in the cookware.
- Electrical Resistance: As these currents flow through the metal, they encounter resistance.
- Heat Generation: This resistance causes the metal to heat up due to the Joule heating effect.
- Heat Transfer: The heat generated in the cookware base is then transferred to the food through conduction.
The amount of heat generated depends on the strength of the magnetic field, the electrical properties of the cookware, and the frequency of the current. By adjusting these factors, induction cooktops can provide precise control over cooking temperatures.
Advantages of Induction Cooktops

Induction Cooker Principle – source
Induction cooktops offer a plethora of advantages that make them increasingly popular in modern kitchens. From energy efficiency to safety features, let’s explore why many home cooks and professional chefs are making the switch to induction cooking.
Energy Efficiency: How Induction Saves Power
Energy efficiency is one of the most significant advantages of induction cooking. Induction cooktops are remarkably efficient in converting electrical energy into heat for cooking.
Here’s why induction cooktops are energy-efficient:
- Direct Induction cooktops: Heat the cookware directly, minimizing energy loss.
- Rapid Heating: They heat up quickly, reducing the overall cooking time and energy consumption.
- Precise Control: The ability to adjust temperature instantly means you’re not wasting energy on unnecessary heat.
- Auto Shut-off: Many induction cooktops have sensors that detect when a pot is removed and automatically shut off, saving energy.
According to Whirlpool, induction cooking can be up to 90% efficient at transferring energy, compared to about 74% for traditional electric ranges and 40% for gas.
Speed: Faster Cooking with Induction Technology
If you’re always in a rush to get dinner on the’ll appreciate the speed of induction cooking. Induction cooktops can bring water to a boil up to 50% faster than gas or electric cooktops.
Why is induction cooking so fast?
- Immediate Heat: There’s no waiting for a burner to heat up; the cookware starts heating instantly.
- Efficient Energy Transfer: More of the energy goes directly into heating the food, not the surrounding air or the cooktop itself.
- Powerful Heating: Induction cooktops can deliver more power to the cookware than gas or electric stoves.
This speed not only saves time but also helps preserve nutrients in your food by reducing cooking times.
Safety Features of Induction Cooktops
Safety is a paramount concern in any kitchen, and induction cooktops excel in this area. They offer several safety features that make them an excellent choice for households with children or elderly members.
Key safety features include:
- Cool Surface: The cooktop surface stays relatively cool, reducing the risk of burns.
- No Open Flame: Unlike gas stoves, there’s no risk of gas leaks or open flames.
- Automatic Shut-off: Many models turn off automatically when no cookware is detected or after a set time.
- Child Locks: Some models have lockable controls to prevent accidental activation.
- Spillover Protection: If a pot boils over, the cooktop often shuts off automatically.
These safety features make induction cooking a worry-free experience, allowing you to focus on the joy of cooking rather than potential hazards.
The Cleanliness Advantage: Easy Cleaning and Spill Management
Cleaning up after cooking can be a chore, but induction cooktops make it significantly easier. Their smooth, flat surface is a breeze to clean compared to the nooks and crannies of gas burners or the coils of electric stoves.
Here’s why induction cooktops are cleaner:
- Cool Surface: Spills don’t burn onto the surface, making them easier to wipe away.
- No Gaps or Crevices: The smooth surface means there are hard-to-reach areas where food can get stuck.
- Non-porous Surface: The glass-ceramic surface doesn’t absorb spills or odors.
- Boil-over Prevention: Some models have sensors that prevent pots from boiling over.
These features not only make cleaning easier but also contribute to a more hygienic cooking environment.
How Induction Cooktops Minimize Heat Loss
Heat loss is a significant factor in cooking efficiency, and induction cooktops excel at minimizing it. Traditional cooking methods often waste energy by heating the air around the pot or the cooktop itself. Induction cooking, on the other hand, generates heat directly in the cookware.
Here’s how induction cooktops minimize heat loss:
- Targeted Heating: The magnetic field only interacts with the cookware, not the surrounding air.
- Cool Surface: The cooktop surface doesn’t get hot, so it’s not radiating heat into the kitchen.
- Efficient Energy Transfer: Most of the energy goes directly into heating the food, not the cookware or the environment.
- Rapid Temperature Changes: You can adjust the temperature instantly, preventing energy waste from residual heat.
This efficient use of energy not only saves on electricity bills but also keeps your kitchen cooler, which can be a significant advantage in hot weather or in professional kitchens.
Cookware Compatibility with Induction Cooktops

Induction Cooktop Cross-section – source
One of the key considerations when switching to an induction cooktop is cookware compatibility. Not all pots and pans will work on an induction st so it’s essential to understand what types of cookware are compatible and how to test your existing kitchenware.
What Types of Cookware are Compatible with Induction Cooktops?
Induction cooktops work withware that contains ferromagnetic materials. This means the cookware must have a high iron content to interact with the magnetic field generated by the cooktop.
Compatible materials include:
- Cast Iron: All types of cast iron cookware, including enameled cast iron, work well on induction cooktops.
- Magnetic Stainless Steel: Most, but not all, stainless steel pots and pans are compatible. Look for those labeled “induction ready” or “induction compatible.”
- Carbon Steel: This material is excellent for induction cooking and is often used in woks and some frying pans.
- Magnetic Aluminum: Some aluminum cookware is made with a magnetic base specifically for use on induction cooktops.
It’s worth noting that pure copper, glass, and non-magnetic stainless steel are not compatible with induction cooktops without a special magnetic base.
How to Test Your Cookware for Induction Compatibility
Not sure if your existing cookware will work with an induction cooktop? There’s a simple test you can perform:
- The Magnet Test: Take a small magnet and hold it to the bottom of your pot or pan. If the magnet sticks firmly, the cookware is likely compatible with induction cooking.
- Check the Symbol: Many induction-compatible pots and pans are marked with a co symbol on the bottom.Consult the Manufacturer**: If you’re still unsure, check the manufacturer’s website or contact their customer service for confirmation.
Remember, the magnet needs to stick firmly. If it’s a weak attraction, the cookware might not work efficiently on an induction cooktop.
Special Magnetic Layers in Non-Ferrous Cookware
To expand the range of cookware compatible with induction cooktops, some manufacturers have developed innovative solutions. They’ve created cookware with special magnetic layers in the base, allowing materials that aren’t normally induction-compatible to work on these cooktops.
Here’s how it works:
- Magnetic Base: A layer of ferromagnetic material is bonded to the bottom of the cookware.
- Conductive Layer: This magnetic layer is often sandwiched between layers of more conductive materials like aluminum or copper.
- Even Heating: The conductive layers help distribute heat evenly across the bottom and up the sides of the cookware.
This technology allows for a wider range of cookware options, including some made from materials like aluminum or copper, which are prized for their heat conductivity but aren’t naturally induction-compatible.
Why Flat-Bottomed Pans Work Best for Cooking
The efficiency of induction cooking relies heavily on good contact between the cookware and the cooktop surface. This is why flat-bottomed pans work best for induction cooking.
Here’s why
1. Magnetic Field Contact: A flat bottom ensures maximum contact with the magnetic field, leading to more efficient heating.
2. Even Heating: Autes heat more evenly across the base of the cookware.
3. Stability: Flat-bottomed pans are more stable on the smooth surface of an induction cooktop.
4. Sensor Detection: Many induction cooktops have sensors that detect the presence of cookware. A flat bottom ensures proper detection.
While some slightly curved bottoms may work, severely warped or rounded bottoms (like those on some woks) may not function well on an induction cooktop without a special adapter.
Disadvantages and Considerations of Induction Cooktops
While induction cooktops offer many advantages, it’s important to consider potential drawbacks before making the switch. Understanding these considerations can help you make an informed decision about whether induction cooking is right for your kitchen.
Cookware Restrictions: What You Need to Know
The primary disadvantage of induction cooktops is the cookware restriction. As we’ve discussed, only ferromagnetic cookware works with induction technology. This means:
- Potential Replacement Costs: You may need to replace some or all of your existing cookware if it’s not induction-compatible.
- Limited Options: Some specialty cookware may not be available in induction-compatible versions.
- Learning Curve: You’ll need to learn which your pots and pans work with the cooktop and potentially adjust your cooking habits.
However, as induction cooking becomes more popular, the range of compatible cookware is expanding, mitigating this issue somewhat.
Potential Interference with Medical Devices (e.g., Pacemakers)
One consideration that’s often overlooked is the potential for induction cooktops to interfere with certain medical devices. The electromagnetic field generated by induction cooktops could potentially affect devices like pacemakers or insulin pumps.
Key points to consider:
- Safe Distance: Most manufacturers recommend maintaining a distance of at least 60cm (2 feet) between the cooktop and the medical device.
- Consult a Doctor: If you or a family member uses such a device, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before using an induction cooktop.
- Options: For those with concerns, traditional electric or gas cooktops may be a safer choice.
It’s important to note that while this potential interference exists, many people with pacemakers use induction cooktops without issues. Always prioritize safety and consult with medical professionals when in How to Adapt Non-Compatible Cookware for Induction
If you have favorite pieces of cookware that aren’t induction-compatible, all is not lost. There are ways to adapt non-compatible cookware for use on induction cooktops:
- Induction Disks: These are flat, magnetic disks that sit between your cookware and the induction surface. They transfer the heat to non-compatible pots and pans.
- Advantages of Induction Disks:
- Allow you to use your existing cookware be cost-effective than replacing all your pots and pans
- Disadvantages of Induction Disks:
- Reduce the efficiency of the top
- slow down cooking times
- May not heat as evenly as direct induction-compatible cookware
While induction disks can be a useful transitional tool, for the best performance, it’s generally recommended to use cookware specifically designed for induction cooking.
Cost and Installation of Induction Cooktops
Another consideration when contemplating a switch to induction cooking is the initial cost and installation process. Induction cooktops tend to be more expensive than traditional gas or electric models.
Factors to consider:
- Higher Upfront Cost: Induction cooktops are generally more expensive to purchase than gas or electric models.
- Potential Electrical Upgrades: Induction cooktops require a 240-volt electrical connection. If your kitchen doesn’t already have this, you may need to upgrade your electrical system, adding to the cost.
- Professional Installation: While some handy homeowners might be able to install a new cooktop themselves, for safety reasons, it’s often recommended to have a professional install an induction cooktop.
- Long-Term Savings: Despite the higher initial cost, the energy efficiency of induction cooking can lead to lower electricity bills over time, potentially offsetting the initial investment.
Can Induction Cooktops Cause Health Issues?
A common question about induction cooking is whether it poses any health risks. While induction cooktops are generally considered safe, some concerns have been raised:
- Electromagnetic Fields (EMF): Induction cooktops produce electromagnetic fields. However, these fields drop off quickly with distance and are generally considered safe at normal cooking distances.
- No Ionizing Radiation: The type of electromagnetic energy used in induction cooking is non-ionizing, meaning it doesn’t have the energy to alter cellular structure like X-rays or gamma rays.
- Limited Exposure: The electromagnetic field is only active when cooktop is on and cookware is present, limiting exposure.
- Research Findings: According to a study by the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health, the electromagnetic radiation from induction cooktops doesn’t pose a health risk to users.
While the consensus is that induction cooking is safe for most people, those with specific health concerns or medical devices should consult with their healthcare provider before using an induction cooktop.
Comparing Induction Cooktops to Traditional Cooking Methods
To truly appreciate the benefits and drawbacks of induction cooking, it’s helpful to compare it directly with traditional cooking methods like gas and electric stoves. Each method has its own unique characteristics that can influence your cooking experience and results.
Induction vs. Gas Stoves: A Detailed Comparison
Gas stoves have long been favored by many chefs for their instant heat control and visual feedback. However, induction cooktops offer some compelling advantages:
| Feature | Induction | Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Control | Precise and instant | Responsive, but less precise |
| Energy Efficiency | Very high (84-90%) | Low (40-55%) |
| Safety | Cool surface, no open flame | Open flame, gas leak risk |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean smooth surface | Grates and burners to clean |
| Cost to Run | Generally lower | Depends on gas prices |
| Cookware Compatibility | Requires specific cookware | Works with most cookware |
| Installation | Requires 240V outlet | Requires gas line |
While gas stoves offer the advantage of working during power outages and being compatible with all cookware, induction cooktops win out in terms of efficiency, safety, and ease of cleaning.
Induction vs. Electric Cooktops: Pros and Cons
Electric cooktops, particularly the smooth-top variety, might seem similar to induction at first glance. However, there are significant differences:
| Feature | Induction | Electric |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic | Resistive heating |
| Speed | Very fast | Slower to heat up and cool down |
| Energy Efficiency | Very high (84-90%) | Moderate (74-77%) |
| Temperature Control | Precise and responsive | Less responsive |
| Safety | Cool surface | Surface stays hot after use |
| Cookware Compatibility | Requires specific cookware | Works with all cookware |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Less expensive upfront |
While electric cooktops are more affordable and don’t require special cookware, induction cooktops offer superior performance in terms of speed, efficiency, and temperature control.
Induction Cooking for Specific Types of Cuisine
Induction cooking can be particularly beneficial for certain types of cuisine:
- Asian Stir-Fry: The high control of induction cooktops make them excellent for quick stir-frying.
- Delauces: The precise temperature control allows for perfect simmering and reduces the risk of scorching delicate sauces.
- Melting Chocolate: The low-temperature capabilities of induction cooktops make them ideal for melting chocolate without burning.
- Boiling and Steaming: The speed at which induction cooktops can bring water to a boil makes them great for pasta, vegetables, and steamed dishes.
However, some techniques like char-grilling or using a round-bottom would be more challenging on an induction cooktop without special adaptors.
Which Cooking Method is the Most Efficient?
When it comes to energy efficiency, induction cooking is the clear winner:
- Induction: 84-90% efficient
- Electric: 74-77% efficient
- Gas: 40-55% efficient
Induction cooking’s high efficiency comes from its ability to heat the cookware directly, minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment. This not only saves energy but also keeps your kitchen cooler, which can be a significant advantage in hot climates or professional kitchens.
FAQs About How Induction Cooktops Work:
Q are eddy currents in induction cooking?
A: Eddy currents are circular electric currents induced within the metal base of cookware by the changing magnetic field of an induction cooktop. These currents generate heat through resistance, directly warming the cookware and its contents.
Q: How does electromagnetic induction heat cookware?
A: Electromagnetic induction heats cookware by creating a high-frequency alternating magnetic field. This field induces eddy currents in the ferromagnetic base of the cookware. The resistance to these currents within the metal generates heat, which then cooks the food.
Q: What types of cookware are suitable for induction cooktops?
A: Cookware suitable for induction cooktops must have a ferromagnetic base. This includes cast iron stainless steel, and some specially made aluminum pans with magnetic bottoms. You can test compatibility by seeing if a magnet sticks firmly to the bottom of the pan. induction cooking compare to gas and electric stoves?
A: Induction cooking is generally more energy-efficient, faster, and provides more precise temperature control than both gas and electric stoves. It’s also safer as the cooktop surface stays relatively cool. However, induction requires compatible cookware and may have a higher initial cost.
Q: Is it safe to use induction cooktops near pacemakers?
A: While induction cooktops are generally safe, they can potentially interfere with pacemakers or other medical implants. It’s recommended that individuals with such devices maintain a distance of at least 60cm (2 feet) from an active induction cooktop and consult their healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Summary:
Induction cooktops represent a revolutionary leap in cooking technology, harnessing the power of electromagnetic fields to deliver efficient, precise, and safe cooking experiences. By heat directly within the cookware, induction cooking offers unparalleled energy efficiency, reaching up to 90% compared to the 40-55% efficiency of gas stoves. This not only translates to faster cooking times and lower energy bills but also contributes to a cooler, more comfortable kitchen environment.
The unique technology behind induction cooking brings with it a host of benefits, from the safety of a cool-to-touch surface to the ease of cleaning a smooth, flat cooktop. The precise temperature control allows for everything from delicate sauce-making to high-heat stir-frying, making it a versatile choice for various cuisines.
However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks, such as the need for compatible cookware and the higher initial cost. For those with pacemakers or other medical implants, extra precautions may be necessary.
As we look to the future of home cooking, induction technology stands as a promising solution that balances efficiency, safety, and performance. Whether you’re a professional chef or a home cook, understanding how induction cooktops work can help you make an informed decision about your cooking setup and potentially revolutionize your culinary experience.
